Voltage Polarity and Current Direction Inst Tools
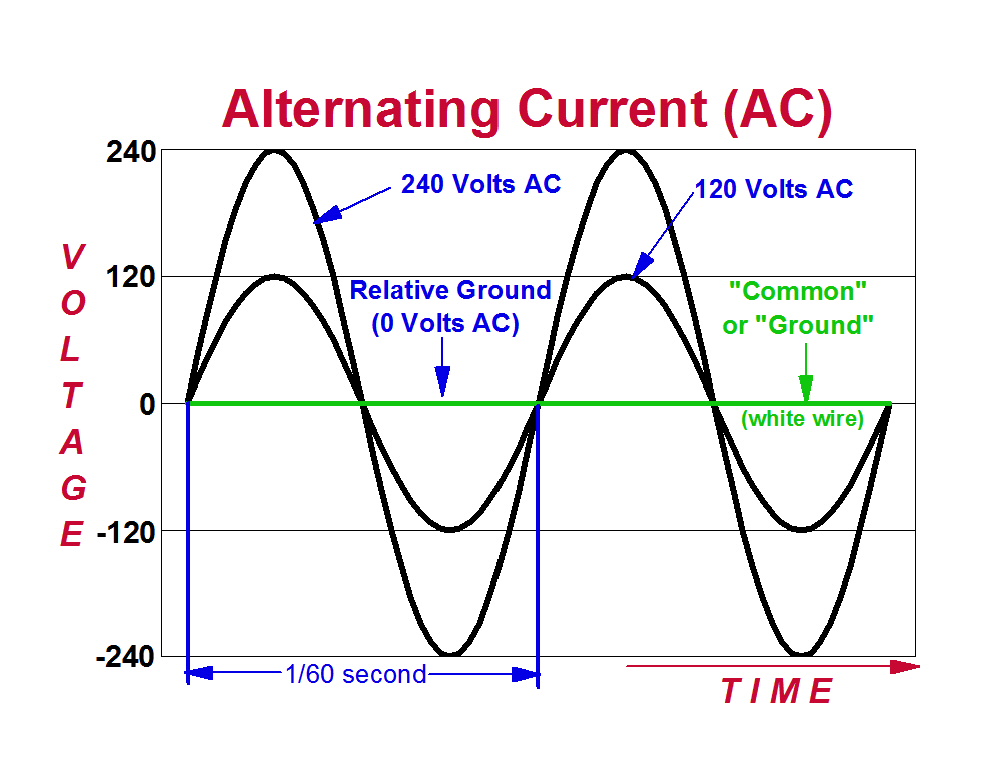
Alternating current ( AC) is an electric current which periodically reverses direction and changes its magnitude continuously with time, in contrast to direct current (DC), which flows only in one direction.
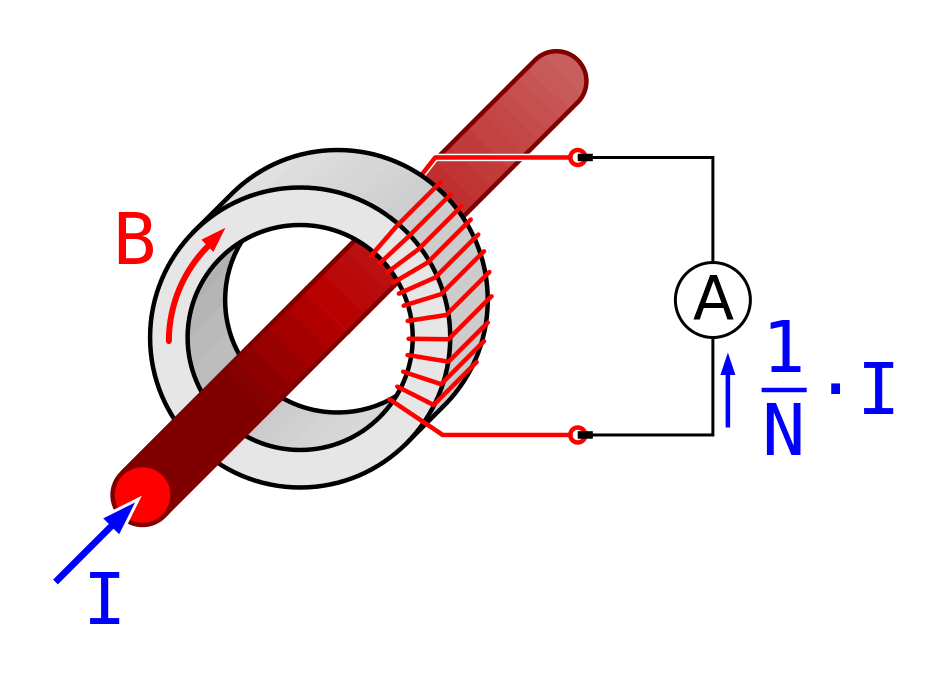
Current Transformer Basics Understanding Ratio, Polarity, and Class
Ac Important Polarity In summary, the correct polarity of AC matters because it affects the direction of current flow, which can be important in certain circuits. This is why it is important to connect live to live and neutral to neutral in wall outlets, even though AC itself has no polarity.

SIMPLY ELECTRICAL STUDY Some Examples with AC Circuits
Chapter 1 Basic AC Theory AC Waveforms PDF Version When an alternator produces AC voltage, the voltage switches polarity over time, but does so in a very particular manner. When graphed over time, the "wave" traced by this voltage of alternating polarity from an alternator takes on a distinct shape, known as a sine wave: Figure below
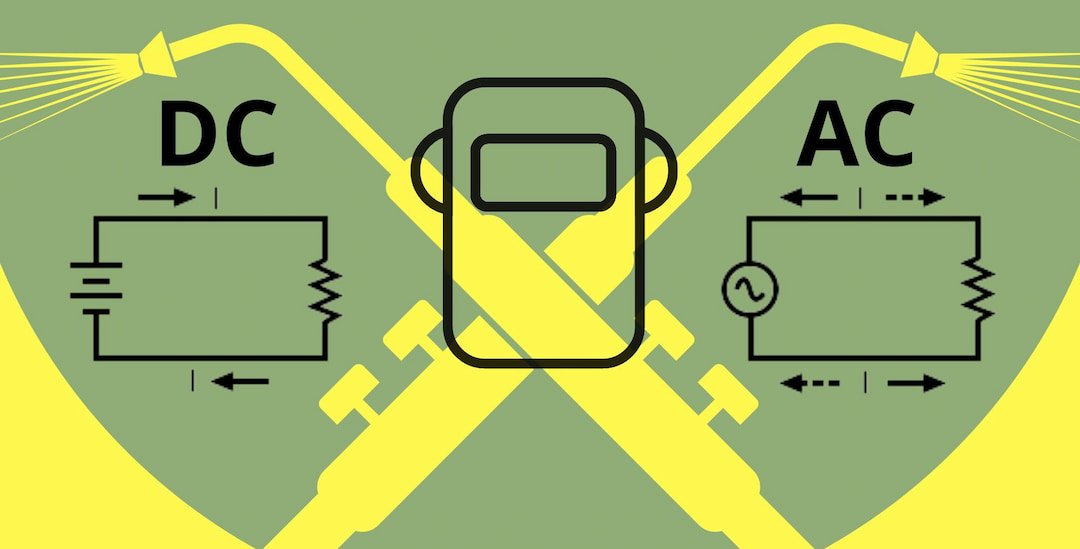
What is Reverse Polarity in Welding? When Do You Use It?
Polarity of AC Circuits Complex numbers are useful for AC circuit analysis because they provide a convenient method of symbolically denoting phase shift between AC quantities like voltage and current. However, for most people, the equivalence between abstract vectors and real circuit quantities is not an easy one to grasp.

Pulsed electrical current can have many different shapes and waveforms.... Download Scientific
It is a constant current. But an alternating current (AC) changes its polarity from every half cycle. For 50Hz current, the waveform changes its polarity at each 10ms. And the polarity changes 100 times in one second. AC Polarity In a DC system, the magnitude and polarity are sufficient to describe.

Polarity of AC Circuits
AC, or Alternating Current, is a type of electric current that periodically reverses direction, oscillating between positive and negative values. In an AC circuit, the electric charge flows first in one direction and then in the opposite direction, constantly reversing its direction at a certain frequency.
Polarity Symbols Direct Current Electrical Polarity Alternating Current, PNG, 1600x1600px
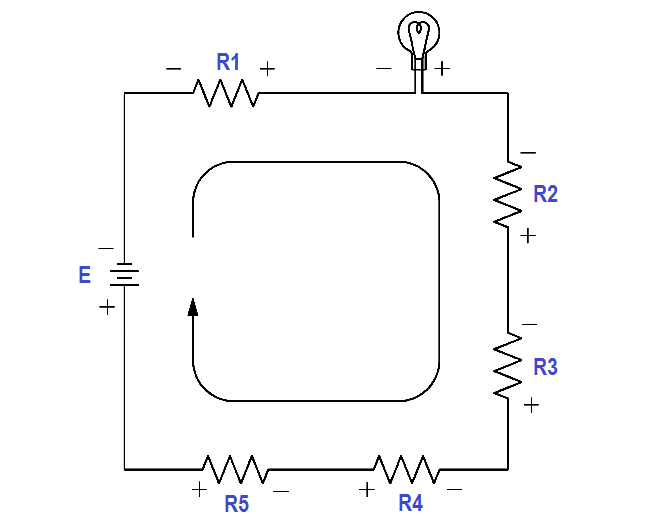
Being that alternating current has no set "polarity" as the direct current does, these polarity markings and their relationship to phase angle tend to be confusing. This section is written in an attempt to clarify some of these issues. Voltage is an inherently relative quantity.
What is Alternating Current (AC)? Sunpower UK
The periodic change in polarity in AC produces a magnetic effect crucial for these devices, lacking in DC.. (DC) power, but the power supplied to the computer from an electrical outlet is alternating current (AC). The power supply unit (PSU) in a computer is responsible for converting the incoming AC power from the wall outlet into the.

Polarity Change in AC Generator Physics
Current will continue to flow until the circuit burns open. A fire aboard is the likely consequence. Reversed polarity also presents a serious shock risk. Turning off a breaker appears to remove power from the circuit because it turns off all appliances connected to that circuit. But with reversed polarity you have disconnected the appliance.

Induced AC current and field using a signal excitation coil in... Download Scientific
Being that alternating current has no set "polarity" as direct current does, these polarity markings and their relationship to phase angle tends to be confusing. This section is written in the attempt to clarify some of these issues. Voltage is an inherently relative quantity. When we measure a voltage, we have a choice in how we connect a.

Electrical Mesh Current Polarity, Equation Setup Valuable Tech Notes
#1 So in the past whenever I used to think about AC current flow, I always envisioned it like the electrons were ping-pong-balls hanging from a string: The would only move back and forth as the voltage on the conductor went from positive to negative and back again.

Alternating Current (AC) Direct Current (DC) Definition, Differences
Alternating current, or AC, reverses polarity at a specified period. This polarity switch is a product of the AC power generation process. AC Power Generation An electromechanical device that produces AC power is called an alternator.
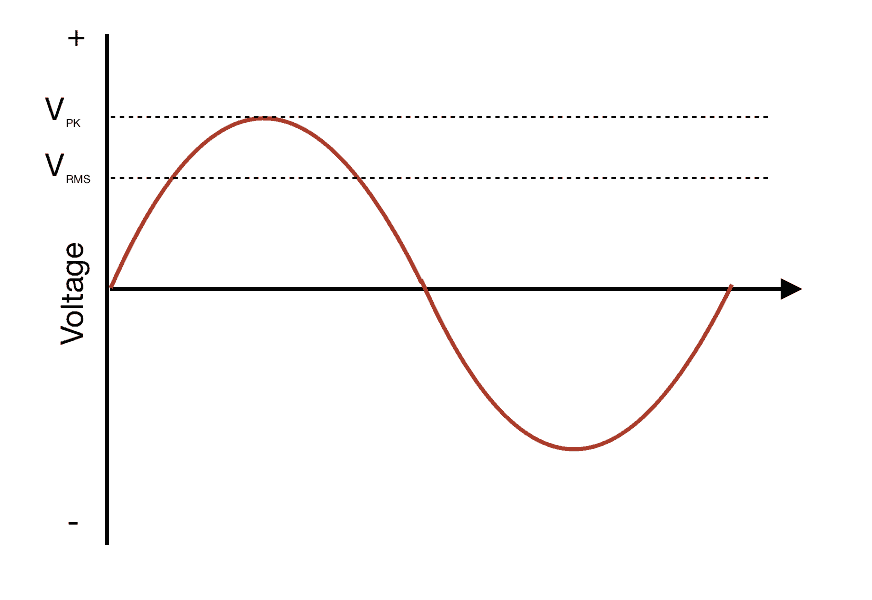
What is Alternating Current? Circuit Basics
What is Alternating Current (AC)? PDF Version Most students of electricity begin their study with what is known as direct current (DC), which is electricity flowing in a constant direction, and/or possessing a voltage with constant polarity.

AC Vs DC Welding Learn Which One Is The Best & Why?
AC stands for "Alternating Current," meaning voltage or current that changes polarity or direction, respectively, over time. AC electromechanical generators, known as alternators, are of simpler construction than DC electromechanical generators. AC and DC motor design follows respective generator design principles very closely.
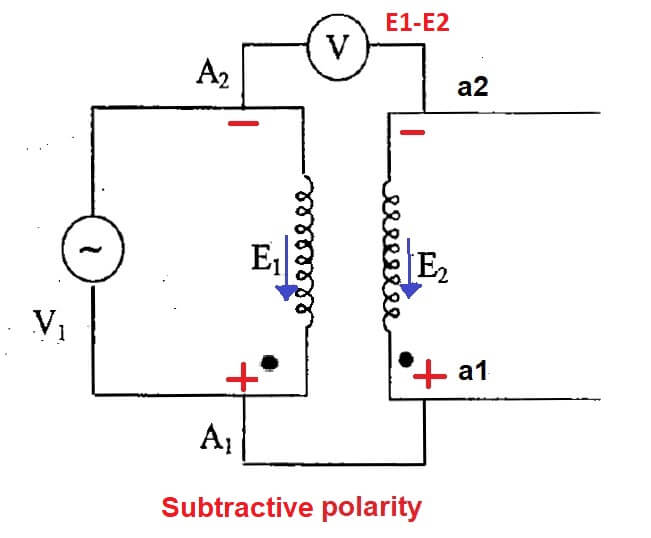
AC MACHINES1 (66761) Theory Illustrate the test to determine the polarity of a transformer
Being that alternating current has no set "polarity" as direct current does, these polarity markings and their relationship to phase angle tends to be confusing. This section is written in the attempt to clarify some of these issues. Voltage is an inherently relative quantity.
-vs-direct-current-(dc).png)
Alternating Current (AC) Direct Current (DC) Definition, Differences
Being that alternating current has no set "polarity" as direct current does, these polarity markings and their relationship to phase angle tends to be confusing. This section is written in the attempt to clarify some of these issues. Voltage is an inherently relative quantity. When we measure a voltage, we have a choice in how we connect a.